â€⢠When Anaerobic Respiration Takes Place, What Happens To The Makeup Of Your Blood?
AP Land Board Syllabus AP SSC tenth Class Biological science Important Questions Chapter 2 Respiration.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions second Lesson Respiration
10th Grade Biology second Lesson Respiration 1 Marking Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the end products of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respirations?
Answer:
End products of aerobic respiration: Carbon dioxide, Water, Energy
End products of anaerobic respiration: Ethanol / Lactic acid, Carbon dioxide, Energy
Question two.
In which organisms, blood does not supply the Oxygen?
Answer:
Arthropoda organisms (or) Insects (OR) Tracheal respiratory Organisms.
![]()
Question iii.
Hari said that stem also respires forth with leaves. How do you support him?
Answer:
Lenticels on stem also help in gaseous commutation in some woody plants along with stomata.
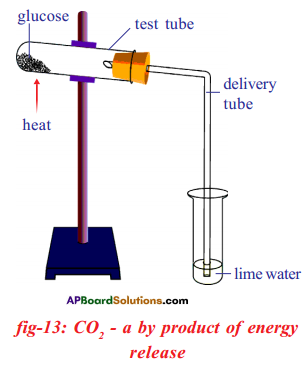
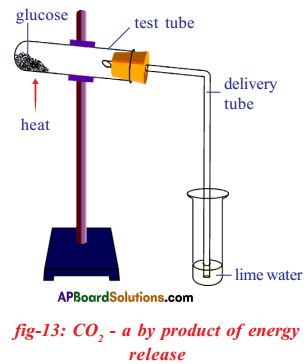
Question 4.
Arrange the apparatus as above and heat the glucose. What will happen to lime h2o when glucose burns?
Reply:
Lime water turns milky due to carbon dioxide (COii).
Question 5.
What is the role of mitochondria in anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
The release of energy from glucose in the presence of oxygen occurs in mitochondria. In anaerobic respiration, as oxygen is absent, mitochondria have no function in respiration.
Question half dozen.
Fermented idli, dosa produce smell. Name the microorganism responsible for producing such smell.
Answer:
Yeast is responsible for producing such odour in fermented idli, dosa.
Question 7.
In what compound, the energy released during the breakdown of glucose is stored?
Answer:
"ATP" (Adenosine Triphosphate).
Question viii.
Characterization a and b in the given diagram.
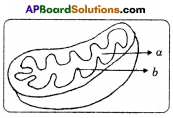
Answer:
(a) Matrix, (b) Cristae.
Question ix.
Proper noun chemical substance produced in human muscles during Anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
Lactic acid is produced in human muscles during Anaerobic respiration.
![]()
Question 10.
Why is Diazene Light-green solution added to the Glucose solution in anaerobic respiration experiment?
Reply:
Diazene Light-green solution is added to the Glucose solution in anaerobic respiration experiment to cheque the presence of oxygen in glucose solution.
Question eleven.
Name the food cloth on which trypsin acts and name the terminate products.
Respond:
i) protein ii) end products – peptones.
Question 12.
"Respiration is the energy releasing process." Write your opinion on this statement.
Respond:
The given statement is absolutely correct. We respire to use the oxygen to oxidise our nutrient and release energy. This is like like burning but a slower process. With the help of respiratory enzymes, energy released can be stored in the grade of ATP for subsequently use.
Question thirteen.
Identify the effigy.

Respond:
Aeriform roots in Mangrove plants.
Question fourteen.
Can we say that combustion and respiration are almost aforementioned deportment? What evidences do you lot accept for this?
Answer:
- In both these processes carbohydrate is converted to carbon dioxide and water.
- Both these processes require oxygen.
- Both combustion and respiration releases energy.
Question 15.
What is the role of epiglottis in respiration and swallowing food?
Reply:
The epiglottis is a flexible flap at the superior end of the pharynx in the pharynx. Epiglot¬tis acts equally a lid over glottis and prevents food from entering into larynx. Air from pharynx enters the larynx while food enters into oesophagus.
Question sixteen.
What is the office of haemoglobin?
Answer:
During respiration haemoglobin carries oxygen to the cells and CO, from cells to lungs.
Question 17.
What is respiration?
Respond:
Respiration is the process past which food is broken downward to release free energy.
Question eighteen.
What does the word respiration hateful in Latin?
Answer:
In Latin the discussion respiration means "to breathe".
Question 19.
Who did comprehensive piece of work on properties of gases, their commutation and respiration?
Reply:
Lavoisier and Priestly.
Question twenty.
What was the gas liberated on heating powdered charcoal in a bell jar?
Answer:
Information technology was fixed air. In those days carbon dioxide was known equally fixed air.
Question 21.
What is oxygen debt?
Answer:
It is the inadequate supply of oxygen when nosotros undertake strenuous exercise.
Question 22.
What is vitiated air?
Answer:
It is the term used so to show air from which the component needed for called-for had been removed.
Question 23.
What is the total lung capacity of homo?
Answer:
The total lung capacity of human beingness is nigh 5800 ml.
Question 24.
Who was the renowned pharmacist who wrote a textbook of Homo Physiology?
Respond:
John Daper was the renowned chemist who wrote a textbook of Homo Physiology.
Question 25.
What happens when air passes through nasal cavities?
Reply:
- Air is filtered in nasal cavity by mucus lining and the hairs growing from its sides, remove some of the tiny particles of clay in the air.
- The temperature of the air is brought shut to that of the body.
Question 26.
What is the part of epiglottis?
Answer:
Epiglottis controls the motility of air and food towards their respective passages.
Question 27.
What is breathing?
Answer:
- Breathing is the process of inhaling and exhaling.
- The mechanism by which organisms obtain oxygen from the environs and release CO2 is chosen breathing.
![]()
Question 28.
What are pleura?
Answer:
Pleura are the two membranes that protect lungs from injury.
Question 29.
What is the concentration of oxygen at a height of thirteen km from the ocean level?
Reply:
At a peak of xiii km above body of water level the concentration of oxygen is much lower most one-fifth every bit great equally at body of water level.
Question thirty.
What is cellular respiration?
Answer:
Oxidation of glucose or fatty acids takes place in the cells releasing free energy. Hence this process is known every bit cellular respiration.
Question 31.
Where does aerobic respiration occur in eukaryotic cells?
Answer:
Aerobic respiration occur in cytoplasm and mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
Question 32.
What is Glycolysis?
Answer:
Information technology is the first stage of respiration. In this breakdown of glucose molecule into two molecules of 3 carbon chemical compound chosen pyruvic acid or pyruvate releasing energy.
Question 33.
What is the fate of pyruvate in the absence of oxygen in animals?
Reply:
In the absence of oxygen pyruvate volition be converted to lactic acid and release small amount of energy in animals.
Question 34.
In which type of respiration pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide and h2o?
Respond:
In aerobic respiration pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide and h2o.
Question 35.
What is the main reason for feeling hurting in muscles later on strenuous exercise?
Answer:
Due to the anaerobic respiration in muscles large amounts of lactic acid is accumulated and this results in muscular pains.
Question 36.
What is fermentation?
Respond:
In the absenteeism of oxygen, yeast cells convert pyruvic acid to ethanol. This process is called fermentation.
Question 37.
What is the method used to separate ethanol from the yeast glucose mixture in anaerobic respiration?
Reply:
The method used to separate ethanol from the yeast glucose mixture in anaerobic respiration is fractional distillation.
Question 38.
In which organisms does exchange of gases take identify through improvidence?
Answer:
In Amoeba, hydra and planarians exchange of gases takes place through diffusion.
Question 39.
In tracheal respiratory system which carry air direct to the cells in the tissues?
Respond:
Trachioles, the fine branches of trachea comport air directly to the cells in the tissues.
![]()
Question 40.
What are the respiratory organs in fishes?
Answer:
Gills or bronchiae are the respiratory organs in fishes.
Question 41.
What is cutaneous respiration?
Answer:
If the respiration occurs through skin, it is known as cutaneous respiration, e.g : Leech, Earthworm and Frog.
Question 42.
What are the other areas on the institute torso through which gaseous exchange take place?
Answer:
The areas on the plant torso through which geseous exchange take place are the surface of roots, lenticels on the stalk.
Question 43.
What is the total grade of ATP? How is it formed?
Answer:
I) ATP stands for Adenosine triphosphate.
2) ATP is used to supply energy in the cells for the carrying all the metabolic processes.
Question 44.
What are the factors that control respiration?
Respond:
Oxygen and temperature are the two important factors that command the process of respiration.
Question 45.
What are the substances that are used for the production of energy in all living organisms?
Answer:
Glucose and fatty acids are used for the production of free energy in all living organisms.
Question 46.
How many types of respiration are nowadays? What are they?
Respond:
There are 2 types of respiration. They are :
- Aerobic respiration and
- Anaerobic respiration.
Question 47.
Where is free energy stored in ATP?
Answer:
Energy is stored in the terminal phosphate bond in ATP which is having three phosphates attached to a molecule of Adenosine.
Question 48.
What are the power houses of the cell?
Answer:
Mitochondria are the power houses of the cell.
Question 49.
What is the main difference between respiration and combustion?
Answer:
In respiration several intermediates are produced and in combustion, at that place are no such intermediates are produced.
Question 50.
What is the equation that represents respiration?
Reply:
The equation that represents respiration is
![]()
Question 51.
.
What are the sites of cellular respiration?
Respond:
Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration.
Question 52.
What are cristae in mitochondria?
Answer:
The inner membrane of mitochondria is thrown into several folds called cristae.
Question 53.
What is the internet gain of ATP molecules in Glycolysis?
Answer:
- 4 ATP molecules are produced when 1 molecule of glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvate but two are consumed.
- The remaining two ATP molecules are net proceeds in glycolysis.
![]()
Question 54.
How many ATP molecules are produced when one glucose molecule is completely oxidised?
Reply:
A net gain of 38 ATP molecules are formed from the total oxidation of one glucose molecule.
Question 55.
What are the three stages nowadays in consummate oxidation of glucose molecule?
Reply:
The three stages present in complete oxidation of glucose molecule are
- Glycolysis
- Kreb'due south wheel and
- Electron send.
Question 56.
Why does oxidation of fatty acids give more than energy?
Answer:
Oxidation of fatty acids give more free energy due to the presence of more than carbon atoms in them.
Question 57.
What are aquatic and terrestrial animals?
Reply:
Animals that live in h2o are chosen aquatic animals and that live on land are known equally terrestrial animals.
Question 58.
Why is the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms much faster than terrestrial organisms?
Answer:
- The amount of oxygen dissolved in water is depression when compared to the amount of oxygen present in air.
- Therefore the charge per unit of animate in aquatic animals is much faster than in terrestrial animals.
Question 59.
Which part of the roots is involved in the substitution of respiratory gases?
Reply:
The part of roots that are involved in the commutation of respiratory gases are root hairs.
Question 60.
What is the average animate rate in an adult mem at rest?
Answer:
The average breathing rate in an adult man at rest is near 15 to 18 times per minute.
Question 61.
Why is the trachea prevented from collapsing?
Answer:
The walls of the trachea are supported by several 'C' shaped cartillagenous rings. They forbid the trachea from collapsing and closing.
Question 62.
Why deos the percentage of carbon dioxide increase in exhaled air?
Respond:
During oxidation of glucose carbon dioxide is produced as waste product. Hence the concentration of carbon dioxide increases in exhaled air.
Question 63.
How does breathing take place in mangrove plants?
Reply:
In mangrove plants animate takes place through specialised structures called jiff¬ing roots or pneumatophores.
![]()
Question 64.
How does respiration take place in plants where roots are present in wet places?
Answer:
The plants which take their roots in very wet places have much larger air spaces, connect the stems with the roots, making diffusion from upper parts.
Question 65.
Which form a continuous network all over the constitute?
Answer:
The stomatal openings lead to a serial of spaces between the cells inside the constitute which form a continuous network all over the establish.
Question 66.
What are the reasons for the animals to develop dissimilar types of respiratory organs?
Answer:
Trunk size, availability of water, habitat in which they live and the type of circulatory system are some of the reasons for the animals to develop dissimilar types of respiratory organs.
Question 67.
Why do fishes die when taken out of water?
Answer:
Fishes exercise not take lungs to utilise oxygen for animate. They have gills which can utilize only dissolved oxygen from water.
Question 68.
What would be the consequences of deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer:
Deficiency of haemoglobin in blood can bear upon the oxygen supplying capacity of blood to trunk cells. It can also atomic number 82 to a disease called Anaemia.
Question 69.
What are the stages of respiration in human being?
Answer:
Respiration in human occurs in two stages 1) Inhalation (or) Inspiration 2) Exhalation (or) Expiration.
Question 70.
Which part plays major role in respiration of man?
Answer:
Diaphragm plays a major part in respiration in human being.
Question 71.
Which part plays major part in respiration of woman?
Answer:
In adult female ribs play a major function in respiration.
Question 72.
How are lungs protected?
Answer:
Lungs are protected past two membranes called pleura. A fluid between these membranes protects the lungs from injury.
Question 73.
What is the composition of exhaled air?
Answer:
Exhaled air contains sixteen% of oxygen, 4% of carbon dioxide and 79% of nitrogen.
Question 74.
Why are red blood cells ruby-red in colour?
Answer:
Cherry claret cells are ruby-red in colour due to the presence of haemoglobin in their cytoplasm.
![]()
Question 75.
How is haemoglobin made upwardly of?
Reply:
Haemoglobin is made upward of a protein chosen globin, Atomic number 26 (Hearn) and organic molecule called porphyrin.
10th Class Biology 2nd Lesson Respiration 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
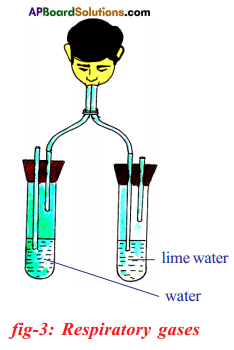 (a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?
(a) Which gas turns lime water milky in this experiment?
Answer:
Carbondioxide (or) CO2
(b) Which gas do you call up might be present in less quantities in the air we breath out as compared to air effectually us?
Answer:
Oxygen (or) O2
Question 2.
Balu said that, "Plants perform Photosynthesis during day time. They respire during night fourth dimension".
Do you agree with Bain? Why? Why not?
Answer:
- I do not agree with Balu's statement.
- Photosynthesis depends on light for energy but respiration does not depend on light.
- Hence, photosynthesis takes place during 24-hour interval time only whereas respiration takes place both day and night.
Question three.
The sportsman who participated in 100 mtr race go more musculus pains. Just the sportsman who participates in 5 km's race get less muscle pains. What is the reason?
Answer:
- Aggregating of lactic acrid results in muscular pain.
- During 100 1000 race a well trained athlete can agree his jiff and afterwards he pants.
- In this case, the muscles are using free energy released during the anaerobic break downwards of glucose, lactic acrid is produced.
- The presence of lactic acrid in the blood is the principal cause of muscle fatigue. Whether it is 100 mtr race or v km race.
- If the body is rested long enough the tiredness goes.
Question 4.
What happens if at that place is no epiglottis in human beings?
Answer:
- Food may enters into the larynx.
- Nutrient may enters into the lungs leading to the death.
- May not speak properly.
- Entry of food and air may not be regulated properly.
![]()
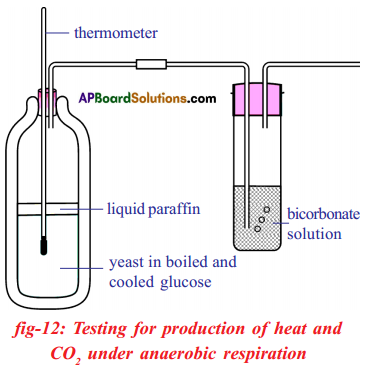
Question 5.
Write ii chemicals and two materials required to deport the experiment "Heat and Carbon dioxide are evolved during anaerobic respiration".
Materials required: Thermosflask, splitted corks, thermometer, wash bottle, drinking glass tubes.
Chemicals required: Liquid alkane, glucose solution, bicarbonate solution, Janus green B and Yeast cells.
Question six.
Discover the beneath diagram.
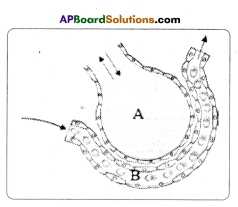 A) To which biosystem is this picture related?
A) To which biosystem is this picture related?
Reply:
Respiratory arrangement.
B) Write the names of the parts of A, B.
Answer:
A – alveolus; B – blood capillary network
C) To which system are they linked with?
Answer:
Respiratory system; circulatory system.
D) Which procedure is happening here? What happens as a result of information technology?
Answer:
Gaseous commutation between air sac of lungs and claret capillaries. Due to this the CO2, nowadays in blood capillaries enter alveolus and oxygen present in alveolus en¬ter blood capillaries.
Question vii.
A person reached a specific distance in one case on foot and once by running. In which situation his legs hurting? Why?
Answer:
- When a person runs to accomplish a specific altitude gets hurting in his legs.
- This is due to the product of lactic acrid in the muscles.
- Due to the Anaerobic respiration glucose in muscles converts into lactic Acid.
- Aggregating of lactic acid causes pain in leg muscles.
Question 8.
What is the advantage of the wet and warm passage of air from the nostrils to capillaries?
Respond:
When the air passes in nasal cavity and in the throat some changes take place.
- The mucus layer and hair in the nasal cavity removes the dust particles in the air.
- The temperature of the air brought to the body temperature.
- Moistening the air.
Question 9.
In the experiment of anaerobic respiration with yeast
i) Why was liquid paraffin poured on glucose?
ii) What did you understood almost anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
i) The supply of oxygen from the air can exist stopped by pouring liquid paraffin on glucose.
ii) Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. In this glucose molecule is incompletely oxidised. The end products of anaerobic respiration are ethyl alcohol or lactic acid and COtwo.
During anaerobic respiration small corporeality of energy is liberated (2ATP). Anaero¬bic respiration occurs in many anaerobic bacteria and human muscles cells. The anaero¬bic respiration can be represented as:
Chalf-dozenH12Osix → 2CiiH5OH + 2COtwo+ 56 K.Cal.
Question 10.
See the below table. Write what you know from it.
| Gas | % in inhaled air | % of exhaled air |
| Oxygen | 21 | 16 |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.04 | four |
| Nitrogen | 79 | 79 |
Answer:
- The inhaled air consists of 21% of oxygen whereas the exhaled air contains xvi% of oxygen only. This is due to utlilisation of oxygen during cellular respiration in the trunk. Hence the difference occurs.
- Inhaled air contains 0.04% of carbondioxide whereas breathe air contains iv% of carbondioxide.
The concentration of CO2 is increased a lot due to the release of CO2 during cellular respiration in the body. - Both inhale and exhale air contains 79% of nitrogen because nitrogen has no role to play in cellular respiration.
![]()
Question 11.
What is the pathway of air from nostril to air sac?
Answer:
Depict a catamenia chart of Respiratory passage of Humans.
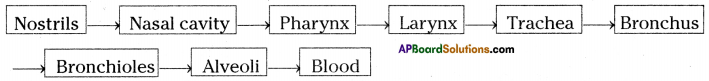
Question 12.
What happens when a baker prepares a dough by mixing yeast in it?
Answer:
- The yeast is unremarkably used for fermenting bread is saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Baker's yeast has the advantage of producing uniform, quick, and reliable results because it is obtained from pure culture.
- Water is mixed with flour, common salt and the fermenting agent.
- The mixed dough is then immune to rise i or more times.
- Then loaves are formed and the bread is baked in air oven.
Question xiii.
How does respiration in amoeba and hydra occur through diffusion? (OR)
What are the similarities in respiration of amoeba and hydra?
Respond:
- Amoeba and hydra are aquatic organisms.
- Respiration in them occurs through diffusion.
- As oxygen is used by these organisms in respiration, its concentration is reduced in cytoplasm. Hence oxygen diffuses into cytoplasm from surrounding water.
- During respiration CO2 is continuously produced, its concentration increases in the cytoplasm, hence it diffuses into surrounding water.
Question fourteen.
Write a brusk note on ATP. (OR) Expand ATP.
Answer:
- From the suspension down of glucose the energy is released and stored up in a special compound known as ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
- It is a pocket-size bundle of chemical energy. The free energy currency of these cells is ATP an free energy rich compound that is capable of supplying energy whenever needed inside the cell.
- Each ATP molecule gives 7200 calories of energy. This energy is stored in the class of phosphate bonds.
- If the bond is broken, the stored free energy is released.
Question 15.
How exercise Dolphin and Crocodile respire?
Answer:
- The aquatic animals similar dolphin and crocodile respire with the help of lungs.
- They come out of the water for air.
- These 2 animals were lived on state initially.
- Later they lived in water and developed several adaptations to alive in water.
Question 16.
Why are Mitochondria called "Power houses of cell"? (QR)
What is the free energy producing organ in a cell? How does information technology produce free energy?
Answer:
- Cellular respiration in prokaryotic cells like that of leaner occurs within the cytoplasm.
- In eukaryotic cells cytoplasm and mitochondria are the sites of reaction.
- The produced energy is stored in mitochandria in the grade of ATP.
- Hence, mitochondria are called "Power houses of cell".
![]()
Question 17.
Write the rate of respiration in different age groups of human beings.
Answer:
- Newborn child: 32 times per minute
- Children of 5 years: 26 times per minute
- Homo of 25 years: 15 times per minute
- Man of 50 years: 18 times per minute
10th Form Biology 2nd Lesson Respiration 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write virtually respiration in mangroves that abound in marshy lands.
Answer:
- Mangroves grown near the marshy places respire through aerial roots or respiratory roots.
- The root hairs exchange the gases from their surface.
- They obtain oxygen from the airspaces present between the soil particles.
- The plants grown in marshy places are adapted to develop aerial roots above the soil surface which helps in gaseous exchange.
Question 2.
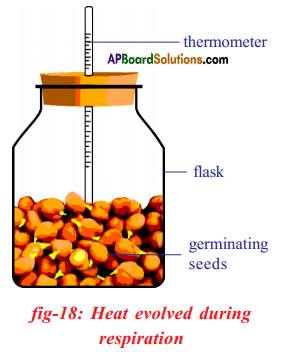 a) What is the aim of this experiment?
a) What is the aim of this experiment?
Answer:
Estrus is liberated during respiration.
b) What alter do y'all observe in thermometer readings?
Answer:
Reading increases in the thermometer.
c) In your opinion, where did this heat come from?
Answer:
The heat comes from the germinating seeds which respire and releasing estrus.
d) What precaution should we have, while doing this experiment?
Respond:
The bulb of the thermometer should exist dip in the germinating seeds (or) sprouts.
Question 3.
You have conducted this experiment in your classroom. Now answer the following questions.
 a) What do y'all evidence by conducting this experiment?
a) What do y'all evidence by conducting this experiment?
Answer:
To test the production of rut and carbon dioxide during anaerobic respiration.
b) Why do you lot rut glucose solution?
Answer:
To remove the dissolved oxygen in the glucose solution.
c) How practise you confirm that glucose solution is gratuitous from oxygen after heating it?
Answer:
Past adding diazine green (Janus green B) solution to glucose solution, it turns to pink.
d) What are the changes you observe in the lime water?
Answer:
Lime water turns milky white.
![]()
Question 4.

i) What alter did y'all observe in the thermometer in the given experiment?
Answer:
Raise in the temperature
two) Where does the heat come up from?
Answer:
From the germinating seeds during respiration
iii) What consequence you will get, if you lot perform this experiment with dry out seeds?
Respond:
No alter of temperature in thermometre.
iv) What are the appliance used in this experiment?
Answer:
Glass jar, germinating seeds, cork, thermometer.
![]()
Question 5.
Observe the set of apparatus and answer the following questions.
 i) Which process do nosotros know with the aid of this experiment?
i) Which process do nosotros know with the aid of this experiment?
Answer:
Combustion.
two) How does this process differ with respiration?
Answer:
Respiration occurs in the presence of water.
Combustion occurs in the absence of water.
3) What are the similarities betwixt this process and respiration?
Answer:
In both processes energy is released.
four) Which gas turns lime – water milky?
Answer:
Carbon-di-oxide (CO2)
Question 6.
Wait at the post-obit experiment. Answer the questions.

a) What is the aim of the experiment?
Answer:
The aim of the experiment is CO2 is released during anaerobic respiration.
b) Which agent is used to find the presence of oxygen?
What changes do you observe when oxygen is present in Glucose solution?
Reply:
To detect the presence of oxygen diazine green (Janus Greenish B) solution is used. The blueish diazine dark-green solution turns pink when oxygen is present in the glucose solution.
c) Why is liquid alkane poured on glucose solution?
Reply:
By pouring liquid methane series on glucose solution, the supply of oxygen from the air can be cut off.
d) Which gas is released during the experiment? How can y'all evidence it?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is released.
The released COtwo passes into lime water it turns milky.
![]()
Question 7.
Observe the following diagram and answer the post-obit questions.
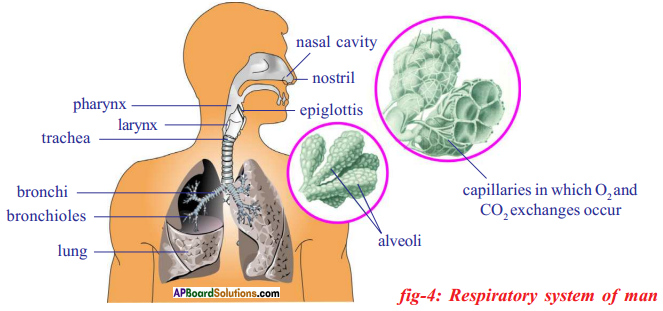
- What do we telephone call the membranes that cover the lungs?
- What is the functional unit of measurement of lungs ?
- Which part produces the sound ?
- What does 'X' denote ?
Respond:
- Pleura
- Alveoli
- Larynx
- Trachea
Question viii.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

a) What does the given diagram point?
b) What is the part 'X' in the diagram?
c) What is the office of the given movie?
d) To which organization the given motion-picture show belongs to?
Answer:
a) The given diagram indicates mitochondria.
b) Matrix
c) Performing cellular respiration and releasing energy in the form of ATP.
d) Respiratory organization.
Question 9.
Observe the experimental setup and answer the given questions.
 A) What is the aim of this experiment?
A) What is the aim of this experiment?
B) What are the apparatus required for this experiment?
C) What changes do you detect in thermometer during this WKm experiment?
D) What will happen, if dry out seeds are taken instead of germinating seeds in this experiment?
Answer:
A) Heat is liberated during respiration.
B) Glass jar, Germinating seeds, Cork and Thermometer.
C) We can notice the raise in temperature afterwards observing the thermometer readings.
D) In that location will exist no alter of temperature in the thermometer. Nosotros can't show the aim of the experiment.
Question x.
Observe the below diagram and respond the following questions:
 i) What does the above setting (diagram) bespeak?
i) What does the above setting (diagram) bespeak?
Answer:
The above setting (diagram) indicates to prove that carbon dioxide and heat are liberated during anaerobic respiration by yeast cells.
ii) Why is boiled and cooled glucose covered with paraffin?
Answer:
To preclude supply of air, boiled and cooled glucose is covered with paraffin.
iii) What is the utilize of adding diazine greenish to glucose solution? What change you notice in glucose solution?
Reply:
Diazine green is added to glucose solution to know whether oxygen is present or non in glucose solution. When the availability of oxygen is less the diazine green changes to pink colour.
4) Why is lime water used in this experiment?
Answer:
To know whether carbon dioxide is released or not in this experiment lime water is used. Carbon dioxide changes lime h2o to milky white.
v) Why is bulb of thermometer dipped in the glucose water?
Reply:
To know the rise in temperature of glucose solution when heated, the bulb of thermometer is dipped in the glucose h2o.
![]()
Question xi.
Explain with the aid of a flow nautical chart, the path style of air in humans.
Respond:
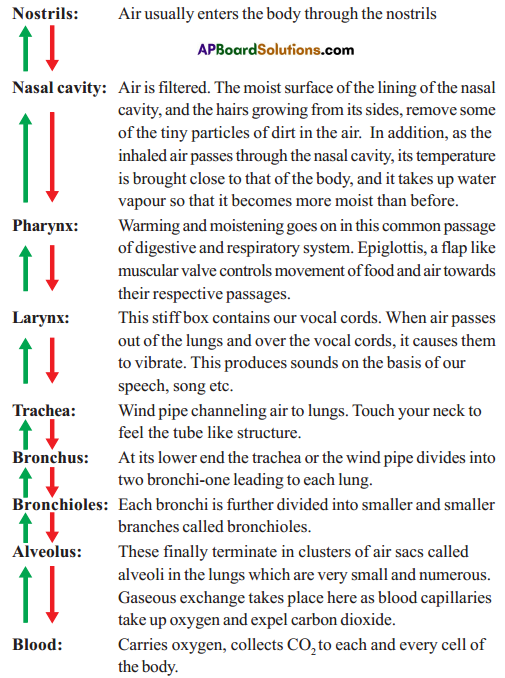
Question 12.
Study the graph and reply the following questions :
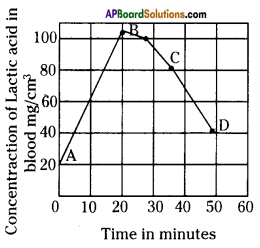 Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.
Graph showing effects of vigorous excercise on the concentration of lactic acid in blood.
i) What was the concentration of lactic acid in blood to beginning with?
ii) What was the greatest concentration of lactic acid reached during the experiment?
iii) What is the concentration of lactic acid afterwards 25 minutes of exercise?
iv) What is the relationship between lactic acid and muscle pain?
Answer:
i) 20 mg/cm3
ii) 20 minutes (Or) at "B" bespeak,
iii) 101 mg/cm3
iv) If concentration of lactic acrid increases, muscle pains also increases.
Question 13.
Observe the following :
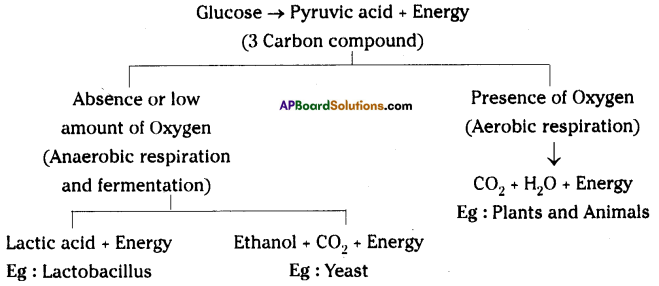
Write the answers to the following questions:
i) How many Pyruvic acrid molecules course from one Glucose?
Reply:
2 Pyruvic acrid molecules.
ii) What weather influence Pyruvic acid to participate in Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
Presence of oxygen
iii) In which we become more than energy in both Aerobic and Anaerobic respirations?
Answer:
Aerobic respiration
iv) The chemical that is formed in human muscles during Anaerobic respiration.
Respond:
Lactic acid
Question 14.
Why does the exchange of gases happen simply in alveoli, though arteries are present in pharynx, trachea and bronchus?
Answer:
- Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs surrounded by capillaries
- They are numerous and only single prison cell thickness
- They increase the efficiency of gas exchange.
- Due to the divergence in a gradient of O2 oxygen diffuse from alveoli to blood capillaries.
Question xv.
What are the events or steps in respiration?
Answer:
The following are the events or steps in respiration.
- Breathing: Air moves into lungs and out of lungs.
- Gaseous commutation in lungs: Commutation of gases between alveoli and claret.
- Gas transport by blood: Transport of oxygen from blood capillaries of alveoli to trunk cells and return of carbon dioxide.
- Gaseous exchange in cells: Exchanging oxygen from claret into the cells and carbon dioxide from cells into the blood.
- Cellular respiration: Using oxygen in cell processes to produce carbon dioxide and h2o, releasing energy to be used for life processes.
![]()
Question 16.
What will happen if the respiratory tract is not moist? (OR)
Why respiratory tract should be moist?
Answer:
- If the respiratory tract is non moist the dirt particles in the inhaled air volition not be removed from air in the nasal cavities and reaches lungs and creates problems to lungs.
- The temperature of the inhaled air is brought close to that of the body for the smooth passage in the respiratory tract. If it is dry out, it is not possible.
- If the surface dries out, gas exchange will happen at a very reduced charge per unit since fast moving gaseous oxygen molecules do not efficiently cross the alveoli membrane.
- The reduced gas substitution is virtually likely not enough to support blood oxygenation for vital functions.
- Hence respiratory tract should be moist for smooth exchange of gases.
Question 17.
Explain the procedure of transportation of gases through the claret.
Answer:
- The relative corporeality of gases and their combining capacity with haemoglobin and other substances in claret determine their ship via blood in the torso.
- When oxygen present in the air is within normal limits (around 21%) then almost all of information technology is carried in the blood by binding to haemoglobin, a protein present in the red blood cells.
- As oxygen is diffused in the blood, it apace combines with the haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin.
- Not just can haemoglobin combine with oxygen, but it can easily broken into haemoglobin and oxygen.
- Carbon dioxide is ordinarily transported every bit bicarbonate, while some corporeality of it combines with haemoglobin and remainder is dissolved in claret plasma.
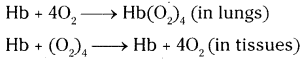
Question 18.
Why is human life impossible at higher altitudes without a supplementary supply of oxygen? (OR)
The concentration of oxygen in air decreases equally we get up from bounding main level. Explain briefly.
Answer:
- If haemoglobin is exposed to air at bounding main level, every molecule in air combines with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin.
- At a elevation of thirteen km above sea level, the concentration of oxygen is much lower well-nigh l/5th of a ocean level.
- Under these atmospheric condition virtually half as many molecules of oxygen combine with haemoglobin to class oxyhaemoglobin.
- Blood cannot deport plenty oxygen to the tissues.
- Hence human life is incommunicable at such a high altitude without a supplementary supply of oxygen.
- Provision for such a supply is built into modern shipping which have pressurized cabins that maintain an enriched air supply.
Question nineteen.
What are the different means in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in diverse organisms? Give one instance of each.
How does oxidation of glucose occur in various organisms?
Respond:
- Glucose is the virtually commonly used carbohydrate for deriving energy in plants, animals and in microorganisms.
- In all these organisms glucose is oxidized in 2 stages.
- The showtime stage is known every bit Glycolysis. It occurs in cytoplasm.
- During glycolysis glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid.
- In the second stage if oxygen is available pyruvic acrid is converted to C02 and water, large amount of energy is released. This is known equally aerobic respiration. It occurs in well-nigh of the institute and fauna cells.
- If oxygen is inadequate or non available, pyruvic acrid is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This is anaerobic respiration taking place in yeast cells that is chosen fermentation.
- If oxygen is non available in muscle cells, the pyruvic acrid is converted into lactic acrid.

![]()
Question twenty.
Write the adaptations seen in plants living in water logged conditions.
(OR)
What are the adaptations seen in magrove plants?
Answer:
- About plants tin can aerate their roots by taking in the oxygen through lenticels or through the surface of their root hairs.
- But plants which accept their roots in very moisture places, are unable to do this.
- They are adjusted to these water logged atmospheric condition by having much larger air spaces which connect the stems with the roots, making improvidence from the upper parts much more efficiently.
- The trouble of air transportion is more than difficult for copse and may not survive with their roots permanently in water.
- To overcome this problem the mangrove tree of the tropics which raise up aerial roots in a higher place the surface and takes in oxygen.
Question 21.
Describe the mechanism of branchial or gill respiration in fishes.
(OR)
Briefly explain the process of exchange of gases in fishes during respiration.
Answer:
- Some aquatic animals similar fishes take adult special organs for respiration which are known equally gills or branchiae.
- Blood is supplied to gills through capillaries which accept thin walls where gases are exchanged. Gills are present in the gill pouches or branchial pouches.
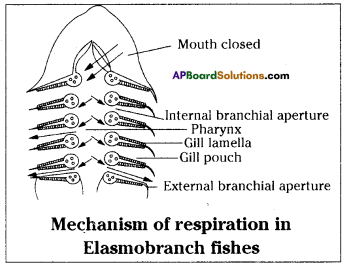
- Gills are provided with leaf-similar folds called gill lamellae.
- Fish keeps its mouth open and lowers the floor of the oral cavity. Equally a effect water from outside volition be fatigued into the oral cavity.
- At present the mouth is airtight and the floor of the oral crenel is raised.
- H2o is pushed into the pharynx and is forced to gill pouches through internal branchia apertures.
- When water passes through gill lamellae exchange of gases takes identify, that is oxygen diffuses from water to blood and COii from blood into water.
- Then water flows through external branchia aperture.
Question 22.
Explain briefly virtually Pranayama- the fine art of breathing. (OR)
How tin can the capacity of lungs be improved by yoga?
Reply:
- To improve breathing capacity the saint Patanjali developed Yogabyasa.
- The fine art of breathing in Yogabyasa is called Pranayama. Prana means gas, ayama means journey.
- In Pranayama practice air is immune to enter iii lobes of lungs in guild to in¬pucker the corporeality of oxygen to lengthened into blood.
- More amount of oxygen available to brain and tissues the body will be more active.
- Information technology is very important to practise Pranayama regularly to make our life healthy and active.
- All people irrespective of historic period and sex should practise Pranayama under the guidance of well trained Yoga Teacher to ameliorate the working capacity of lungs.
Question 23.
What are the experiments carried out past Lavoisier to understand the property of gases?
Answer:
- In his early experiments Lavoisier thought that the gas liberated on heating powdered charcoal in a bell jar kept over water in a trough was like fixed air i.e., carbon dioxide.
- The next series of experiments deals with the combustion of phosphorous in a bong jar. From this he showed that whatever it was in the atmospheric air which combined with the phosphorous was not water vapour.
- This was respirable air, a component of air that besides helped in burning.
- The air that we breathe out precipitated lime h2o while that afterwards heating metal did non.
- From this, he concluded that there were two processes involved in respiration.
- Lavoisier carried out another experiment by which he showed that about 1 sixth of the volume of 'vitiated air' consists of chalky acid gas (fixed air).
- Either eminently respirable air is changed in the lungs to chalky acid air; or an commutation takes place, the eminently respirable air being absorbed, and an almost equal volume of chalky acid air existence given up to the air from the lungs.
- Lavoisier had to acknowledge that in that location were strong grounds for believing that eminently respirable air did combine with the blood to produce the red colour.
![]()
Question 24.
Explain the evolutionary changes in energy-releasing system.
(OR)
What are the different respiratory systems in animal groups?
Reply:
Exchange of gases is a common life process in all living organisms, simply it is not same in all.
- Diffusion:
- Unmarried-celled organisms like amoeba or multicellular organisms like hydra and planarians obtain oxygen and miscarry carbon dioxide directly from the body past the process of diffusion.
- In multicellular animals special organs are evolved.
- Torso size, availability of h2o and the type of circulatory system are some of the reasons for the animals to develop different types of respiratory organs.
- Tracheal respiratory arrangement : In insects tracheal respiratory arrangement is present in which pocket-sized branches of trachea chosen trachioles behave air directly to the cells in the tissues.
- Bronchial respiration : In fishes gills are utilised for the exchanges of gases. Blood is supplied to gills through capillaries which have thin walls for exchange of gases. This is called bronchial respiration.
- Cutaneous respiration: 0 Respiration through peel is called cutaneous respiration.
Eg: i) Globe worms and leeches.
ii) Frog, an amphibian can respire through lungs and skin. - Pulmonary respiration : Most of the higher animals respire with the assistance of lungs. This type of respiration is known as pulmonary respiration. Eg: Mammals.
Question 25.
Depict the construction of mitochondria with the help of a diagram. (OR)
Which cell organelle is called energy currency or power house of cell? What practise you know about its construction?
Respond:
Mitochondria is known as energy currency or power house of cell.
Structure of mitochondria:
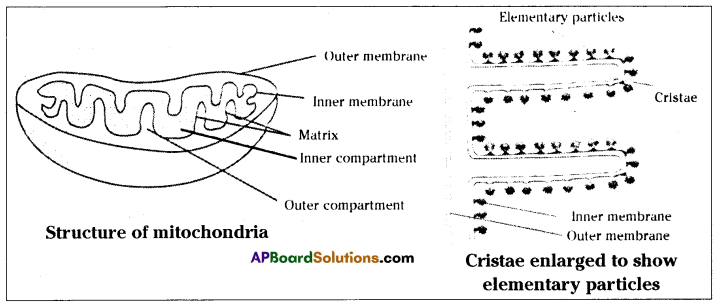
- Mitochondria are sac-similar structures present in the cytoplasm of the cells.
- Mitochondria take 2 compartments-an inner compartment and an outer compartment. The substance in the inner compartment is called matrix.
- The matrix is surrounded past a membrane called inner membrane of mitochondria.
- The inner membrane is thrown into several folds called cristae. The cristae extended into the matrix.
- The space betwixt the folds is continuous with the outer compartment.
- On the inner membrane, projecting into the matrix are a large number of particles called elementary particles.
- These particles have a spherical head and a stem. They are attached to the inner membrane by their stalk and the head portion of the particle is in the matrix.
- The outer compartment is surrounded by another membrane – the outer membrane. The outer membrane is smoothen and has no projections.
- The inner membrane, the matrix and the unproblematic particles in the mitochondria have large number of enzymes and other required proteins for the respiration and free energy production.
![]()
Question 26.
Describe and label mitochondria. Why should we call it cell of power ?
Respond:
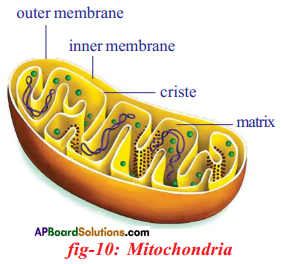 Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The free energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the grade of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence nosotros call information technology prison cell of power or power house of the ceil.
Oxidation of glucose molecule occurs in the mitochondria, ot cell. This is known as cellular respiration. The free energy produced during cellular respiration stored in the grade of ATP molecule. Energy producing cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria hence nosotros call information technology prison cell of power or power house of the ceil.
Question 27.
Describe how oxygen enters the blood in lungs with the aid of block diagram.
(OR)
How does gaseous commutation occur in lungs?
Reply:
- Gaseous exchange takes place inside the lungs by improvidence from the alveoli to blood capillaries and vice versa. Alveoli in lungs are numerous and only i cell thick.
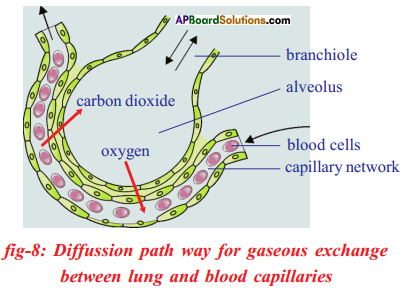
- Alveoli are surrounded past capillaries that are likewise 1 prison cell thick.
- Claret, night red in colour flows from the heart through these capillaries and collects oxygen from the alveoli.
At the aforementioned time, carbon dioxide passes out of the capillaries and into the alveoli. - When we breathe out, we go rid of carbon dioxide.
- The vivid red, oxygen rich blood is returned to the heart and pumped out to all parts of the body.
![]()
Question 28.
What is the role of diaphragm and ribs in respiration? Are both active in human being and woman?
Respond:
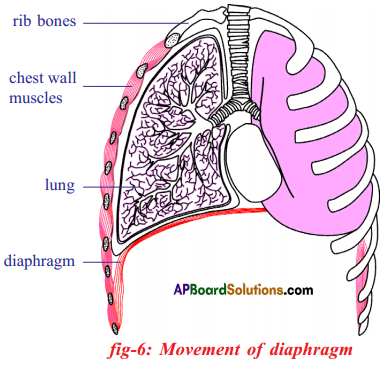
Diaphragm:
- Diaphragm is a muscular dome shaped tissue present at the floor of the chest cavity separating abdomen from respiratory organisation.
- Diaphragm expands down into the abdomen thus increasing chest cavity. This allows the lungs to expand as we inhale.
- Equally the diaphragm contracts upward thus decreasing the chest cavity, it allows the air to expel from the lungs.
Ribs: - The ribs protect the lungs and aggrandize as we inhale to facilitate infinite for the lungs to expand. The ribs and then contract expelling the air from the lungs.
- The intercostal muscles present between the ribs aid in contraction and relaxation of ribs.
- In man, diaphragm plays a major role in the respiration, while in woman, the ribs play a major role.
Question 29.
Why are alveoli so small and uncountable in number? (OR)
How do alveoli increase the expanse for exchange of gases?
Answer:
- The pouch-like air sacs at the ends of the smallest branchioles are called alveoli.
- The walls of the alveolus are very thin and they are surrounded past very thin blood capillaries.
- It is in the alveoli that gaseous substitution takes place.
- In that location are millions of alveoli in the lungs. The presence of millions of alveoli in the lungs provides a very large expanse for the exchange of gases.
- And the availability of large surface area maximises the exchanges of gases.
Question xxx.
Write a cursory note on respiration in plants. (OR)
Does respiration occur in plants? Explain briefly about it.
Answer:
- In most plants exchange of gases takes identify through stomata.
- At that place are other areas on the plant body like surface of roots, lenticels on stalk, etc. the gaseous exchange takes place.
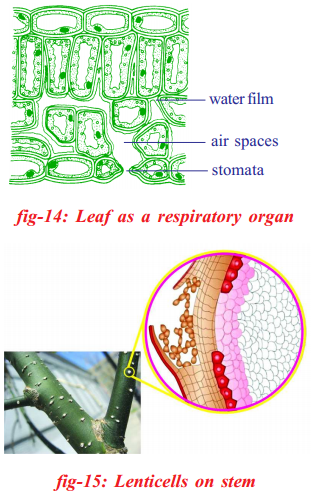
- Some plants have specialized structures like animate roots of mangrove plants as well as the tissue in orchids.
- Breathing roots and tissue in orchids help plants to accept oxygen to produce energy and release carbon dioxide.
- Inside the plants openings lead to a series of spaces between the cells which form a continuous network all over the plant.
- The whole arrangement works by diffusion.
- As the oxygen is used up by the cells a gradient develops between the cells and the air in the spaces.
- So oxygen passes in betwixt the air spaces and the air outside stomata and lenticels.
- In the same mode, as more than carbon dioxide is given out by the cells, a gradient occurs in the reverse direction and it passes out.
![]()
Question 31.
Write a brief note on tracheal respiration in insects.
Answer:
- In insects blood do not contain haemoglobin, and blood is white in color. Hence it cannot carry oxygen.
- For respiration insects adopt a special arrangement called tracheal arrangement.
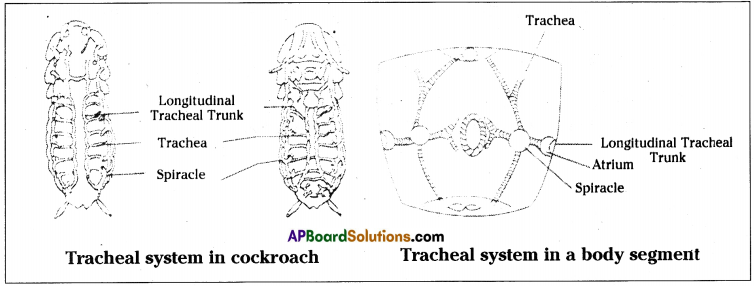
- This system consists of a series of tubes called trachea.
- These trachea open out through small apertures called spiracles on either side of the body.
- All tracheal tubes of each side bring together and form a longitudinal tracheal body.
- Trachea dissever into a number of branches called tracheoles which comport air directly to the tissues.
- As the air moves in and out of the trachea, oxygen present in the air diffuses into the cells and COii diffuses into the air from the cells.
Question 32.
Write almost the mechanism of respiration in human beings. (OR)
How does exchange of gases take place in human beings?
Answer:
- Respiration in man occurs in two stages. They are inspiration and expiration.
- During inspiration air from outside enters into the lungs by increasing the chest cavity.
- Increase in the chest crenel is made by pulling the diaphragm downward and pushing the ribs forward.
- As the air force per unit area in the lungs is reduced, air from exterior enters the lungs through external nostrils, nasal cavities, internal nares, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx, trachea, bronchi and branchioles and finally reach the alveoli where exchange of gases takes place.
- During expiration the diaphragm and ribs come up back to original positions.
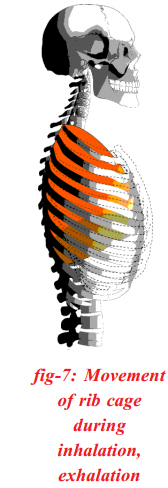
- This reduces the book of chest cavity.
- So the volume of lungs is decreased and air nether pressure comes out of the lungs.
![]()
Question 33.
Written report the graph given below and analyse the reasons for accumulation of lactic acid in blood later on strenuous exercise.

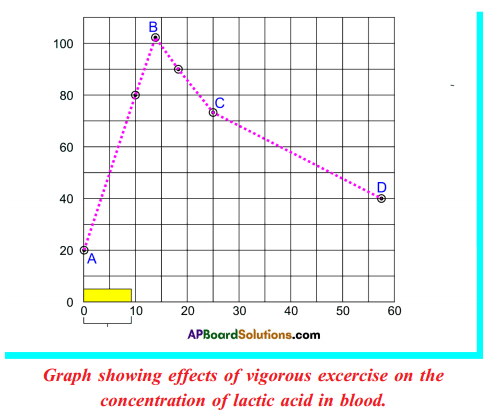
Answer:
- This graph shows the relation between fourth dimension accumulation of lactic acrid in the muscles.
- At the start, the amount of lactic acid in the blood is very less.
- Gradually information technology is increased past vigorous exercise.
- Within 15 minutes information technology goes to maximum level which causes muscle hurting.
- Then the lactic acid is removed from muscles in an 60 minutes.
- Muscles produce energy past anaerobic respiration.
C6H12O6 → lactic acid + CO2 + energy - In the vigorous practise, musculus piece of work rapidly and produce more lactic acid.
- That'due south why lactic acrid concentration is increased in muscle after strenuous practise.
Question 34.
Observe the to a higher place graph of lactic acid accumulation in the muscles of an athlete and respond the following questions.
a) What was the concentration of lactic acid in the blood to start with?
Answer:
Information technology is 20 mg/km3.
b) What was the greatest concentration reached during the experiment?
Respond:
101 mg/cm3.
c) If the trend between points C and D were to continue at the aforementioned charge per unit, how long might it take for the original lactic acid level to be reached over again?
Answer:
55 minutes.
d) What does high level of lactic acrid point about the condition of respiration?
Answer:
It indicates the aggregating of lactic acid in muscles through anaerobic respiration. The presence of lactic acid in the blood is the main crusade of muscular pain and fatigue.
![]()
Question 35.
Depict the construction of human lungs with the aid of a diagram.
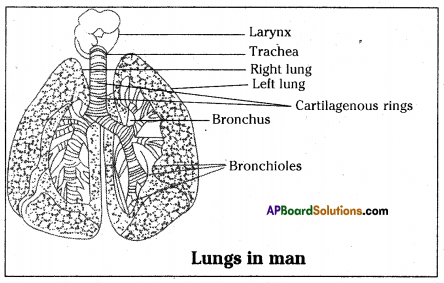
Respond:
- A pair of lungs is present in the chest cavity one on either side of the heart.
- Lungs are spongy and elastic. They are enclosed by two membranes called pleura.
- Space between the two membranes of pleura is filled with fluid. Pleura protects the lungs from injury.
- Correct lung is larger than the left lung.
- Right lung is fabricated of three lobes while the left lung has only two lobes.
- Lung has several thousands of alveoli which are supplied with blood capillaries.
- Pulmonary artery brings deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
- Later on entering the lung, this artery divides into several arterioles and capillaries and supplies deoxygenated blood to alveoli.
- Gas substitution occurs in the alveoli.
- Oxygenated blood is carried from the lung to heart past the pulmonary vein.
Projection work
Question 1.
Observe and analyse the questions in the tabular array given below.
| Newly borned | (Children) | (Children) | Children | Youth/Adults | Athletics | |
| (0-3 months) | (3-6 months) | (6-12 months) | (one-10 years) | |||
| Heart beat | 100 -150 | 90-120 | 80 -120 | 70-130 | 60-100 | forty-60 |
A) In which historic period group charge per unit of heart crush is more than?
B) In which age group rate of heart vanquish is less?
C) Why heart beat in Athletics is less?
D) What are reasons for more than rate of center beats differences between the newly born and children?
Answer:
A) In newly borned babies which are in 0 – 3 months of age group charge per unit of heart beat out is more i.eastward., 100 to 150 times.
B) In athletics the rate of eye beat is less i.e., 40 – threescore times / minute.
C) The heart of athlete pump more than blood per beat due to increased cardio-vascular fitness in the structure of the center. The muscles in the heart wall thicken and the heart pumps more blood with each beat.
D)
- Mothers who have special medical conditions such as thyroid diseases or diabetes may give birth to new borns who are temporarily tachscardic from altered hormone and glucose levels. Tachycardia is a medical term for a very rapid heart beat.
- Some infants are born with accompaniment electrical tissue in the heart causes epi¬sodes of rapid heart rate.
- In wolf – parkinson syndrome – white syndrome there are actress cells and an ac-cessory path way, causing boosted centre beats.
![]()
Question two.
Observe the table given below and analyse the questions.
| Name of the animal | Weight of the torso | Weight of the heart | No. of beats/min |
| Bluish whale | one,thirty,000 kg | 750 kg | vii |
| Elephant | 3000 kg | 12-21 kg | 46 |
| Man | 60 – 70 kg | 300 gm | 76 |
| Coaltit (Bird) | viii gm | 0.xv gm | 1200 |
A) Why centre crush is less in animals with more than weight?
B) Why middle beat is more in animals with less weight?
C) What is the human relationship between weight of the torso and rate of heart beat?
D) Why the weight of center is less than body weight?
Answer:
A) The animals with more weight unremarkably have weighted hearts. In one heart beat the big-sized hearts sends high amounts of blood to circulatory system. Information technology takes time for the fulfilment of heart. Hence heart beat is less in animals with more body weight.
B) Unremarkably the middle is very small in less weight animals. When the animal shrinks or contracts , its heart actually decrease the book of blood proportionately. It can compensate for the reduced volume by increasing the rate at which it tin can supply claret to all torso parts.
C) Every bit the weight of the body of the animal increases the rate of heart beat per infinitesimal decreases. And also as the weight of the body decrease the rate of eye vanquish increases.
D) Normally the body of an organism is made past number of organs which makes the trunk functional. As all the body parts institute the whole organism, the heart 1 of the organ is usually has less weight than body weight of an animal.
![]()
Source: https://apboardsolutions.guru/ap-ssc-10th-class-biology-important-questions-chapter-2/
Posted by: tranwastookey.blogspot.com

0 Response to "â€⢠When Anaerobic Respiration Takes Place, What Happens To The Makeup Of Your Blood?"
Post a Comment